hermes theorem | Heron's Formula hermes theorem There are many ways to prove Heron's formula, for example using trigonometry as below, or the incenter and one excircle of the triangle, or as a . See more
With oversized square retro lenses and a smooth black finish upon the frame, the SL 183 BETTY shades are nailed on to become a classic look for this and many Summer's to .
0 · Pythagoras
1 · Peano axioms
2 · Heron's formula
3 · Heron's Formula
4 · 3.5: Theorems of Fermat, Euler, and Wilson
Immediately recognizable by its black dial featuring large 3, 6 and 9 hour markers and a prominent minutes scale, the Air‑King continues Rolex’s long association with aviation which dates back to the 1930s. More than a tribute, this robust and sporty watch, donned with a 40 mm Oystersteel case, symbolizes the fearlessness of aviation .
Pythagoras
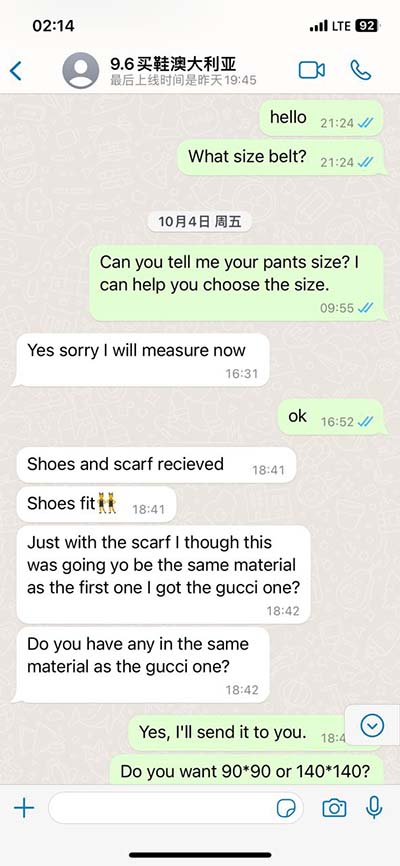
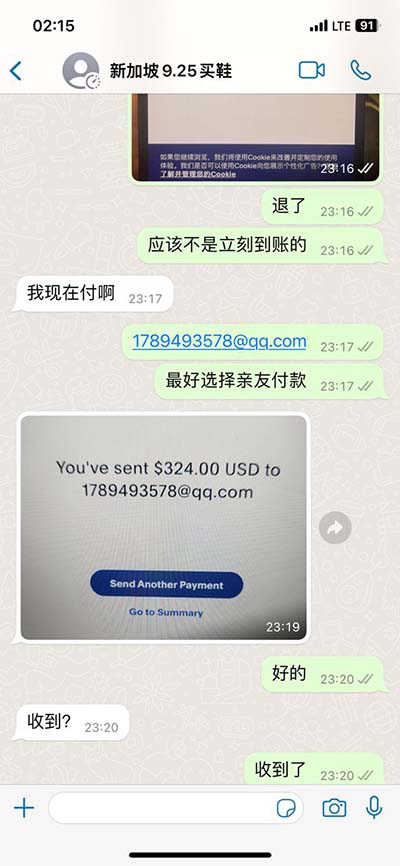
In geometry, Heron's formula (or Hero's formula) gives the area of a triangle in terms of the three side lengths $${\displaystyle a,}$$ $${\displaystyle b,}$$ $${\displaystyle c.}$$ Letting $${\displaystyle s}$$ be the semiperimeter of the triangle, See moreHeron's formula can also be written in terms of just the side lengths instead of using the semiperimeter, in several ways,After expansion, the . See moreHeron's formula as given above is numerically unstable for triangles with a very small angle when using floating-point arithmetic. A stable alternative involves arranging the lengths . See more
Heron's formula is a special case of Brahmagupta's formula for the area of a cyclic quadrilateral. Heron's formula and Brahmagupta's . See more
The formula is credited to Heron (or Hero) of Alexandria (fl. 60 AD), and a proof can be found in his book Metrica. Mathematical historian Thomas Heath suggested that Archimedes knew . See more
There are many ways to prove Heron's formula, for example using trigonometry as below, or the incenter and one excircle of the triangle, or as a . See moreThree other formulae for the area of a general triangle have a similar structure as Heron's formula, expressed in terms of different variables. See more• Shoelace formula See more
In mathematical logic, the Peano axioms , also known as the Dedekind–Peano axioms or the Peano postulates, are axioms for the natural numbers presented by the 19th-century Italian mathematician Giuseppe Peano. These axioms have been used nearly unchanged in a number of metamathematical investigations, including research into fundamental questions of whether number theory is consistent and complete.
You can calculate the area of a triangle if you know the lengths of all three sides, using a . An important theorem in plane geometry, also known as Hero's formula. Given .
In antiquity, Pythagoras was credited with many mathematical and scientific discoveries, .We now present Fermat’s Theorem or what is also known as Fermat’s Little Theorem. It states .In geometry, Heron's formula (or Hero's formula) gives the area of a triangle in terms of the three side lengths Letting be the semiperimeter of the triangle, the area is [1] It is named after first-century engineer Heron of Alexandria (or Hero) who proved it in his work Metrica, though it was probably known centuries earlier.In mathematical logic, the Peano axioms (/ piˈɑːnoʊ /, [1] [peˈaːno]), also known as the Dedekind–Peano axioms or the Peano postulates, are axioms for the natural numbers presented by the 19th-century Italian mathematician Giuseppe Peano.
You can calculate the area of a triangle if you know the lengths of all three sides, using a formula that has been known for nearly 2000 years. It is called "Heron's Formula" after Hero of Alexandria (see below) Just use this two step process: Step 1: Calculate "s" (half of the triangles perimeter): s = a+b+c 2. Step 2: Then calculate the Area: An important theorem in plane geometry, also known as Hero's formula. Given the lengths of the sides a, b, and c and the semiperimeter s=1/2 (a+b+c) (1) of a triangle, Heron's formula gives the area Delta of the triangle as Delta=sqrt (s (s-a) (s-b) (s-c)).

Peano axioms
In antiquity, Pythagoras was credited with many mathematical and scientific discoveries, including the Pythagorean theorem, Pythagorean tuning, the five regular solids, the Theory of Proportions, the sphericity of the Earth, and the identity of the morning and evening stars as the planet Venus.We now present Fermat’s Theorem or what is also known as Fermat’s Little Theorem. It states that the remainder of when divided by a prime that doesn’t divide is 1. We then state Euler’s theorem which states that the remainder of when divided by . Hans Hermes. Part of the book series: Universitext (UTX) 6601 Accesses. 19 Citations. 3 Altmetric. About this book. This book grew out of lectures. It is intended as an introduction to classical two-valued predicate logic. Rolle’s theorem is a special case of the Mean Value Theorem. In Rolle’s theorem, we consider differentiable functions \(f\) that are zero at the endpoints. The Mean Value Theorem generalizes Rolle’s theorem by considering functions that .
An acute triangle ABC with its vertices on the three coordinate axes. The respective distances \ ( \left ( {l,m,n} \right) \) from the origin O to the vertices (A,B,C) are easily computed via the Pythagorean theorem. From. $$ a^ {2} = m^ {2} + n^ {2} \quad {\text {and}}\, {\text {cyclic}}\; {\text {permutaions}} $$.
Given its long history, there are numerous proofs (more than 350) of the Pythagorean theorem, perhaps more than any other theorem of mathematics. The proofs below are by no means exhaustive, and have been grouped primarily by the approaches used in the proofs.In geometry, Heron's formula (or Hero's formula) gives the area of a triangle in terms of the three side lengths Letting be the semiperimeter of the triangle, the area is [1] It is named after first-century engineer Heron of Alexandria (or Hero) who proved it in his work Metrica, though it was probably known centuries earlier.In mathematical logic, the Peano axioms (/ piˈɑːnoʊ /, [1] [peˈaːno]), also known as the Dedekind–Peano axioms or the Peano postulates, are axioms for the natural numbers presented by the 19th-century Italian mathematician Giuseppe Peano.You can calculate the area of a triangle if you know the lengths of all three sides, using a formula that has been known for nearly 2000 years. It is called "Heron's Formula" after Hero of Alexandria (see below) Just use this two step process: Step 1: Calculate "s" (half of the triangles perimeter): s = a+b+c 2. Step 2: Then calculate the Area:
An important theorem in plane geometry, also known as Hero's formula. Given the lengths of the sides a, b, and c and the semiperimeter s=1/2 (a+b+c) (1) of a triangle, Heron's formula gives the area Delta of the triangle as Delta=sqrt (s (s-a) (s-b) (s-c)).In antiquity, Pythagoras was credited with many mathematical and scientific discoveries, including the Pythagorean theorem, Pythagorean tuning, the five regular solids, the Theory of Proportions, the sphericity of the Earth, and the identity of the morning and evening stars as the planet Venus.
We now present Fermat’s Theorem or what is also known as Fermat’s Little Theorem. It states that the remainder of when divided by a prime that doesn’t divide is 1. We then state Euler’s theorem which states that the remainder of when divided by . Hans Hermes. Part of the book series: Universitext (UTX) 6601 Accesses. 19 Citations. 3 Altmetric. About this book. This book grew out of lectures. It is intended as an introduction to classical two-valued predicate logic. Rolle’s theorem is a special case of the Mean Value Theorem. In Rolle’s theorem, we consider differentiable functions \(f\) that are zero at the endpoints. The Mean Value Theorem generalizes Rolle’s theorem by considering functions that .

An acute triangle ABC with its vertices on the three coordinate axes. The respective distances \ ( \left ( {l,m,n} \right) \) from the origin O to the vertices (A,B,C) are easily computed via the Pythagorean theorem. From. $$ a^ {2} = m^ {2} + n^ {2} \quad {\text {and}}\, {\text {cyclic}}\; {\text {permutaions}} $$.
$9,950.00
hermes theorem|Heron's Formula