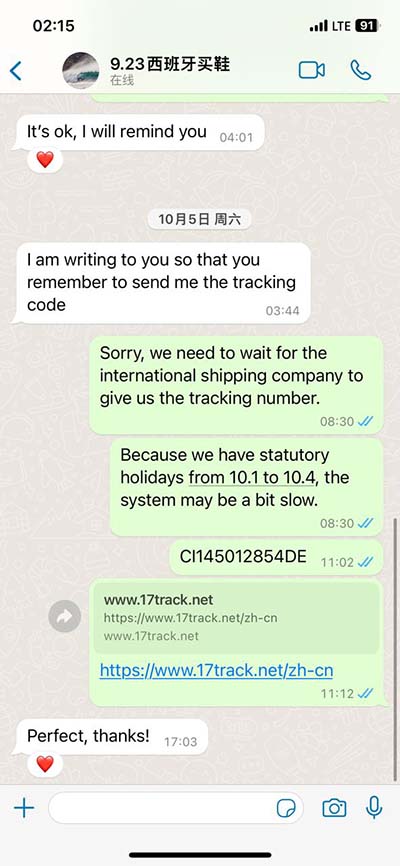
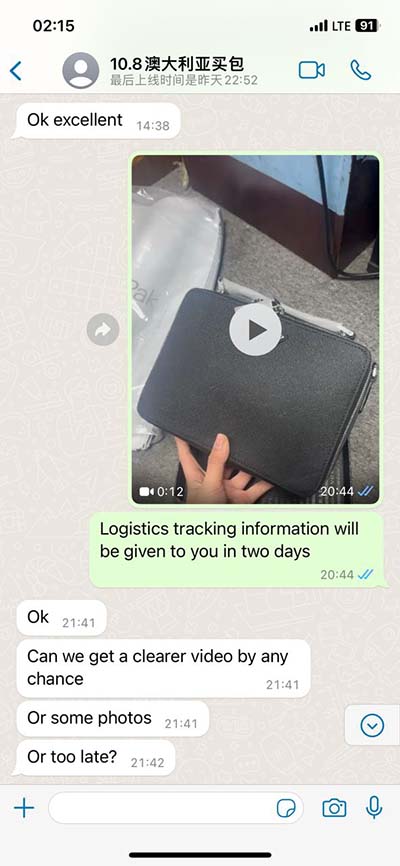
hermes roman mythology | 10 thing that represent hermes hermes roman mythology AtlantiadesHermes was also called Atlantiades (Greek: Ατλαντιάδης), because his mother, Maia was the daughter of Atlas.ArgeïphontesHermes's epithet Argeïphontes (Ancient Greek See more Often on a fake Louis Vuitton bag, “the hardware just looks cheaper,” says D’Amato. A real luxury bag provides a pleasure of touch that counterfeiters simply can’t reproduce. So if the hardware is rough or uneven, feels flimsy, hollow or even (gasp!) plastic, the bag is most likely a fake.Professional Louis Vuitton authenticators say that the #1 way to spot a fake bag is to check the label stitched on the inside. It is never correctly replicated, according to our Expert LV Bag Authenticators. 1. Interior label. Authentic: Thicker text, with all letters placed at the same level. Fake: Text is too thin and the letters are misplaced.
0 · why is hermes called
1 · what is hermes realm called
2 · major myths associated with hermes
3 · how does hermes see himself
4 · hermes can usually be found
5 · greek mythology hermes wife
6 · famous myths about hermes
7 · 10 thing that represent hermes
Lehigh Valley Zoo.
In myth, Hermes functions as the emissary and messenger of the gods, [6] and is often presented as the son of Zeus and Maia, the Pleiad. He is regarded as "the divine trickster", [7] about which the Homeric Hymn to Hermes offers the most well-known account. [8] See moreHermes is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, merchants, and orators. . See more
Hermes began as a god with strong chthonic, or underworld, associations. He was a psychopomp, leader of souls along the road between . See more
AtlantiadesHermes was also called Atlantiades (Greek: Ατλαντιάδης), because his mother, Maia was the daughter of Atlas.ArgeïphontesHermes's epithet Argeïphontes (Ancient Greek See moreThe earliest form of the name Hermes is the Mycenaean Greek *hermāhās, written 𐀁𐀔𐁀 e-ma-a2 (e-ma-ha) in the Linear B syllabic script. Most . See moreThe image of Hermes evolved and varied along with Greek art and culture. In Archaic Greece he was usually depicted as a mature man, bearded, and dressed as a traveler, herald, or shepherd. This image remained common on the Hermai, which served as . See more
In the Mycenaean periodThe earliest written record of Hermes comes from Linear B inscriptions from Pylos, Thebes, and Knossos dating to the Bronze Age See moreEarly Greek sourcesHomer and HesiodHomer and Hesiod portrayed Hermes as the author of skilled . See more
The great Greek epics, Hesiod's "Theogony" and Homer's "Iliad" and "Odyssey," . Hermes, Greek god, son of Zeus and the Pleiad Maia; often identified with the .
Mercury, in Roman religion, god of shopkeepers and merchants, travelers and transporters of . Hermes, son of Zeus and Maia, is the Greek god of invention, theft, and a herald . Hermes (Mercury to the Romans), the fleet-footed messenger with wings on his . The messenger of the gods was Hermes, known as Mercury in ancient Roman religion, and he was also a pastoral god, protecting livestock and travellers. Hermes' symbols include the caduceus – a staff intertwined with .
Hermes. Roman name: Mercury. Epithets: Argeïphontes (Killer of Argus), Psychopompos (Guide of Souls), Hermes the Helper. Symbols: caduceus (kerykeon), winged sandals, petasos (traveling hat) Functions: messenger to . Hermes. In Greek mythology, the messenger of the gods; son of Zeus and Maia, .
In myth, Hermes functions as the emissary and messenger of the gods, [6] and is often presented as the son of Zeus and Maia, the Pleiad. He is regarded as "the divine trickster", [7] about which the Homeric Hymn to Hermes offers the most well-known account. [8] The great Greek epics, Hesiod's "Theogony" and Homer's "Iliad" and "Odyssey," provide much of the basic information on the Greek gods and goddesses. The playwrights add to this and give more substance to the myths alluded to in the epics and other Greek poetry.
why is hermes called
sac yves saint laurent prix maroc
Hermes, Greek god, son of Zeus and the Pleiad Maia; often identified with the Roman Mercury. Hermes was associated with the protection of cattle and sheep. In the Odyssey, however, he appears mainly as the messenger of the gods and the conductor of . Hermes was the ancient Greek god of trade, wealth, luck, fertility, animal husbandry, sleep, language, thieves, and travel. One of the cleverest and most mischievous of the 12 Olympian gods, Hermes was their herald and messenger.Mercury, in Roman religion, god of shopkeepers and merchants, travelers and transporters of goods, and thieves and tricksters. He is commonly identified with the Greek Hermes, the fleet-footed messenger of the gods. Hermes, son of Zeus and Maia, is the Greek god of invention, theft, and a herald for the Olympians. Known as Mercury in Roman mythology, Hermes was born on Mount Cyllene and famously crafted a lyre from a tortoise shell before stealing Apollo's cattle.
what is hermes realm called
Hermes (Mercury to the Romans), the fleet-footed messenger with wings on his heels and cap symbolizes fast floral delivery. However, Hermes was originally neither winged nor a messenger -- that role was reserved for the rainbow goddess Iris *. The messenger of the gods was Hermes, known as Mercury in ancient Roman religion, and he was also a pastoral god, protecting livestock and travellers. Hermes' symbols include the caduceus – a staff intertwined with two snakes – as well as his winged sandals and cap, and a tortoise.Hermes. Roman name: Mercury. Epithets: Argeïphontes (Killer of Argus), Psychopompos (Guide of Souls), Hermes the Helper. Symbols: caduceus (kerykeon), winged sandals, petasos (traveling hat) Functions: messenger to the gods and god of travelers, traders, thieves, herds, and heralds. Hermes carrying a ram on an olpe found in the Louvre.
Hermes. In Greek mythology, the messenger of the gods; son of Zeus and Maia, one of the Pleiades. Homer's Odyssey presented the god as the conductor of the dead (shades) to Hades, in which capacity he became associated with the underworld and dreams.
In myth, Hermes functions as the emissary and messenger of the gods, [6] and is often presented as the son of Zeus and Maia, the Pleiad. He is regarded as "the divine trickster", [7] about which the Homeric Hymn to Hermes offers the most well-known account. [8] The great Greek epics, Hesiod's "Theogony" and Homer's "Iliad" and "Odyssey," provide much of the basic information on the Greek gods and goddesses. The playwrights add to this and give more substance to the myths alluded to in the epics and other Greek poetry.
Hermes, Greek god, son of Zeus and the Pleiad Maia; often identified with the Roman Mercury. Hermes was associated with the protection of cattle and sheep. In the Odyssey, however, he appears mainly as the messenger of the gods and the conductor of . Hermes was the ancient Greek god of trade, wealth, luck, fertility, animal husbandry, sleep, language, thieves, and travel. One of the cleverest and most mischievous of the 12 Olympian gods, Hermes was their herald and messenger.Mercury, in Roman religion, god of shopkeepers and merchants, travelers and transporters of goods, and thieves and tricksters. He is commonly identified with the Greek Hermes, the fleet-footed messenger of the gods.
Hermes, son of Zeus and Maia, is the Greek god of invention, theft, and a herald for the Olympians. Known as Mercury in Roman mythology, Hermes was born on Mount Cyllene and famously crafted a lyre from a tortoise shell before stealing Apollo's cattle.
Hermes (Mercury to the Romans), the fleet-footed messenger with wings on his heels and cap symbolizes fast floral delivery. However, Hermes was originally neither winged nor a messenger -- that role was reserved for the rainbow goddess Iris *. The messenger of the gods was Hermes, known as Mercury in ancient Roman religion, and he was also a pastoral god, protecting livestock and travellers. Hermes' symbols include the caduceus – a staff intertwined with two snakes – as well as his winged sandals and cap, and a tortoise.Hermes. Roman name: Mercury. Epithets: Argeïphontes (Killer of Argus), Psychopompos (Guide of Souls), Hermes the Helper. Symbols: caduceus (kerykeon), winged sandals, petasos (traveling hat) Functions: messenger to the gods and god of travelers, traders, thieves, herds, and heralds. Hermes carrying a ram on an olpe found in the Louvre.
major myths associated with hermes
Fano.lv atradīsiet Latvijas populārākos radio kanālus. Tagad vairs nevajag domāt, kuru staciju klausīties, jo tās visas ir sasniedzamas klikšķa attālumā. Visi radio internetā ir bez maksas. Klausieties sev ērtā laikā un vietā. Izvēlieties radio staciju pēc nosaukuma, žanra vai citiem kritērijiem.Fano.lv atradīsiet Latvijas populārākos radio kanālus. Tagad vairs nevajag domāt, kuru staciju klausīties, jo tās visas ir sasniedzamas klikšķa attālumā. Visi radio internetā ir bez maksas.
hermes roman mythology|10 thing that represent hermes